The Psychological Effects of Chronic Knee Pain
December 30, 2025
The Role of Skin Cancer in Overall Health and Wellness
January 3, 2026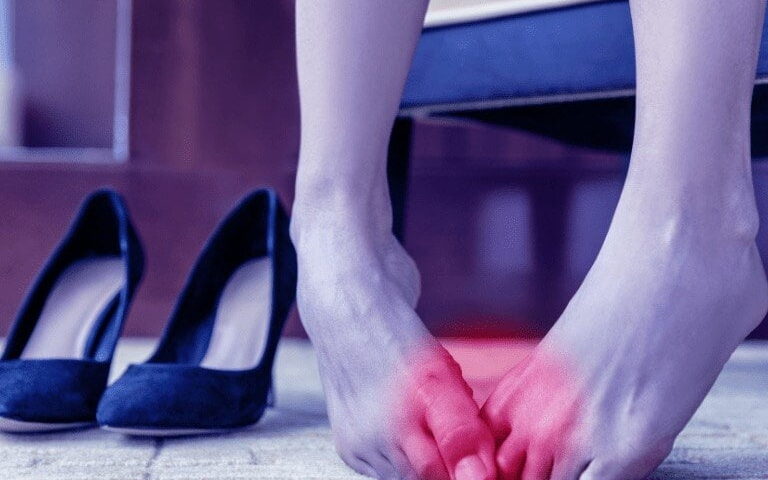
A bunion is a structural deformity of the bones in the foot and often presents as a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of your big toe. This condition, medically known as hallux valgus, occurs when some of the bones in the front part of your foot move out of place, causing the tip of your big toe to get pulled toward the smaller toes. This then forces the joint at the base of your big toe to stick out. The skin over the bunion might be red and sore, and the deformity may make wearing regular shoes uncomfortable. Here’s information on the risk factors for developing bunions:
How Common Are Bunions?
A bunion is a prevalent foot condition that affects a large portion of the adult population. Studies suggest that nearly one in three older adults has a bunion, although they can develop in younger individuals. While they are seen in men and women, women are more likely to develop them, likely due to footwear choices. The prevalence of bunions increases with age, as the cumulative effect of stress on the feet manifests as structural changes.
What Causes Them?
The exact cause of bunions is often a combination of genetic factors and environmental stressors, but they generally develop slowly over time. Pressure on the big toe joint causes the big toe to lean toward the second toe, and eventually, the normal structure of the bone changes, resulting in the bunion bump. This pressure can come from the way you walk or the structure of your foot, which you may have inherited from your parents. Foot injuries or neuromuscular disorders can also contribute to the development of this deformity.
What Are the Symptoms?
The signs of a bunion can vary depending on the severity of the condition. The most obvious symptom is a bulging bump on the outside of the base of your big toe. You might also experience swelling, redness, or soreness around your big toe joint. Corns or calluses often develop where the first and second toes rub against each other. Some individuals also experience persistent or intermittent pain.
What Are the Types?
While most people refer to the condition simply as a bunion, there are variations depending on location and severity. The three main types are:
- Standard Bunion (Hallux Valgus): The most common type, which is located at the base of the big toe.
- Tailor’s Bunion (Bunionette): A smaller bump that forms on the outside of the foot at the base of the little toe.
- Adolescent Bunion: These occur in younger people, typically between the ages of 10 and 15, and are often hereditary.
What Can Treat Bunions?
Treatment plans vary based on the severity of the bunion and the amount of pain it causes. Conservative, non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of defense. Changing shoes to roomy, comfortable footwear that provides plenty of space for your toes can relieve pressure. Using bunion pads or shoe inserts can help distribute pressure evenly when you move your feet, which may reduce symptoms and prevent the bunion from getting worse. In cases where conservative measures do not provide relief or the deformity interferes significantly with daily activities, surgical options may be discussed. Surgeries are used to realign the bone, ligaments, tendons, and nerves.
Make a Podiatrist Appointment
If you suspect you are developing a bunion or experiencing persistent foot pain, you may benefit from a professional evaluation. Early diagnosis and intervention can slow the progression of the deformity and help manage discomfort effectively. A podiatrist can examine your foot, take X-rays to assess the bone structure, and recommend a tailored treatment plan. Contact a podiatrist today.