Conditions Treated With Epidural Steroid Injections
December 5, 2025
Tips For Overcoming Nasal Congestion
December 5, 2025
Back injuries often stem from mechanical issues within the spinal column, but preventive strategies can mitigate risk. Strengthening exercises focus on building muscle resilience, serving as a defense against chronic pain and acute trauma. Here is more information on back injuries, strengthening exercises, and orthopedic surgery:
What Are Back Injuries?
Back injuries refer to damage inflicted upon the bones, muscles, or other soft tissues of the back. Common manifestations include sprains, strains, herniated discs, and fractured vertebrae, affecting mobility and quality of life. These injuries disrupt the normal function of the spine, and they can lead to debilitating pain if left untreated. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and imaging to determine the extent of the damage.
Treatment plans depend on the severity of the injury and the specific structures involved. Conservative management may include rest, physical therapy, and pain management protocols. In cases where structural damage is extensive or neurological function is compromised, orthopedic surgery becomes a necessary intervention. This surgical approach aims to restore anatomy when non-invasive methods do not yield results.
What Causes Them?
The cases of back injuries are often multifaceted, involving both acute traumatic events and cumulative wear and tear. Poor body mechanics during lifting or bending places excessive stress on the lumbar region, leading to muscle strains or ligament sprains. Repetitive motions contribute to micro-trauma in the tissues, and over time, this may result in injury. Degenerative changes associated with aging also play a significant role in the development of back issues.
How Can Strengthening Exercises Prevent Them?
Strengthening exercises function by fortifying the muscles that surround and support the spinal column. A robust core acts as a natural brace for the back, distributing mechanical loads more evenly across the torso. When the abdominal and paraspinal muscles are strong, they absorb impact forces, so the vertebrae and discs are spared from excessive pressure. This protective mechanism is fundamental for maintaining spinal integrity during dynamic movements.
Targeted training improves the endurance of postural muscles, allowing them to maintain proper alignment for extended periods. Fatigue in the back muscles often leads to slouching or hyperextension. This places the spine in compromised positions. Strengthening regimens delay the onset of muscle fatigue, and this helps individuals maintain neutral spine alignment throughout the day.
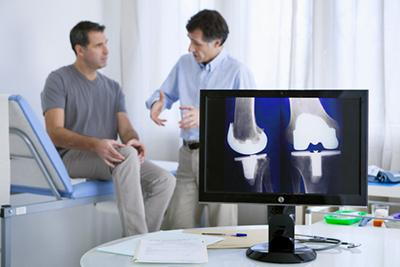
What Is Orthopedic Surgery?
Orthopedic surgery is a medical specialty focused on the diagnosis, correction, prevention, and treatment of patients with skeletal deformities. Surgeons perform procedures to alleviate pain and restore stability to the spinal column. Patients may evaluate surgery when neurological symptoms such as numbness or weakness persist, and the goal is to prevent permanent nerve damage and improve functional capacity.
What Are the Benefits?
The primary benefit of orthopedic surgery is the alleviation of chronic pain that has not responded to conservative treatments. Surgical intervention can correct structural issues, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis, directly addressing the source of discomfort. This may result in a significant improvement in the patient’s quality of life, allowing them to resume daily activities with less pain.
Another key benefit is the restoration of function and mobility. For conditions that cause instability or nerve compression, surgery can stabilize the spine or decompress affected nerves. This may lead to the return of strength in weakened limbs and a reduction in symptoms like numbness or tingling.
Seek Professional Guidance Today
Strengthening exercises help prevent back injuries, whereas orthopedic surgery addresses back issues to restore function. Consult a healthcare professional before initiating any new exercise regimen or choosing surgery. An orthopedic specialist can assess individual risk factors and prescribe a suitable treatment.