Exploring the Future of GLP-1 Medications in Weight Management
January 7, 2026
What Patients Should Know About Functional Medicine
January 8, 2026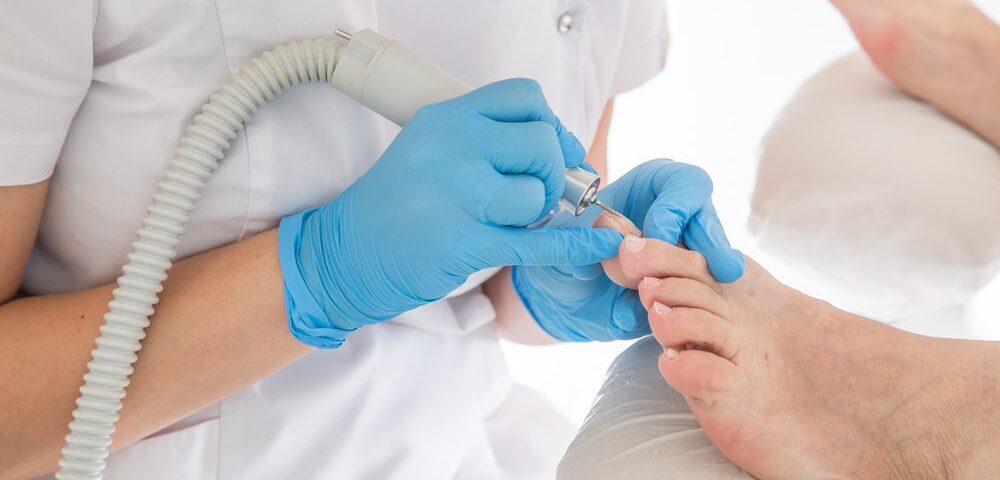
A podiatrist is trained to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the foot, ankle, and related structures of the legs. They manage everything from sports injuries and structural deformities to skin and nail conditions. Toenail fungus, medically known as onychomycosis, is a common infection that begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of a fingernail or toenail. As the fungal infection goes deeper, nail fungus may cause your nail to discolor, thicken, and crumble at the edge. Here’s information on fungal nails and how podiatrists treat them:
What Is Toenail Fungus?
Fungal infections usually occur when microscopic fungi enter the nail through a small trauma, such as a cut or break in the nail, or through the separation between the nail and the nail bed. A fungal infection may affect several nails at once. These fungal organisms thrive in warm, moist environments, which is why they can be contracted in places like:
- Public Swimming Pools
- Public Showers
- Sweaty Shoes
People with reduced blood circulation to the feet or a weakened immune system may also face a higher risk of developing these infections. The fungus can persist indefinitely without treatment, potentially leading to permanent nail damage.
How Is Nail Fungus Diagnosed?
Diagnosing fungal nails typically requires a visit to a podiatrist for a physical examination. The doctor will examine your nails, looking for visible signs such as thickening, discoloration, or debris buildup under the nail. Conditions like psoriasis or bacterial infections can mimic fungal infections, so nail samples are used to confirm the presence of fungus.
To confirm the diagnosis, a podiatrist may take nail clippings or scrape debris from beneath the nail. This sample is then sent to a lab for analysis. The lab can identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection, which helps in determining an effective treatment plan. Treatment protocols vary depending on the specific organism involved.
What Can Treat Toenail Fungus?
Your podiatrist will recommend a treatment plan tailored to the severity of the infection and the type of fungus identified. For mild to moderate infections, your doctor may prescribe a topical antifungal medication. These are typically applied directly to the nail and the surrounding skin daily. Some come in the form of nail lacquers or polishes that you paint onto the nail. Topical treatments often require a long duration of use to be effective because the medication must penetrate the hard nail plate to reach the fungus underneath.
Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal drugs are a common treatment option for clearing up more stubborn infections. They work systemically to reach the nail bed, and are typically used for six to 12 weeks. The goal is to help a new, non-infected nail grow free of fungus, slowly replacing the infected part. Oral medications are generally more effective than topical ones, but they may require blood tests to monitor liver function during the treatment course.
Laser Treatments
Laser therapy is an option that uses focused light energy to treat nail fungus. During the procedure, the laser penetrates the toenail to target the fungus living underneath without damaging the surrounding skin or tissue. This method can be a beneficial alternative for patients who cannot take oral medications or who have not seen success with topical treatments.
Contact a Podiatrist for Your Fungal Nails
Managing fungal nails usually requires time and professional guidance. While over-the-counter remedies exist, they are often not strong enough to clear established infections. A podiatrist can provide a definitive diagnosis and access to prescription-strength treatments that offer a higher likelihood of success. If you notice changes in your nails, schedule a podiatrist appointment to discuss your options.

