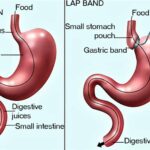
Overcoming Common Challenges After Gallbladder Removal Surgery
January 13, 2026How To Prepare for Your Dermatology Appointment
January 21, 2026
Routine colon cancer screenings are a primary method for detecting early signs before symptoms develop. These preventative procedures allow medical professionals to identify and remove polyps; polyps are small growths that can become cancerous over time. Here is more information about the different types of colon cancer screenings and how to prepare for them:
Common Colon Cancer Screening Types
A screening test identifies diseases when a person does not have symptoms. Colon cancer screening can detect precancerous polyps, and physicians can remove these growths before they turn into cancer. Regular preventative screenings help find cancer at an early stage before symptoms start occurring.
Colonoscopy and flexible sigmoidoscopy are two primary visual exams for colon cancer screening. A colonoscopy examines the entire length of the large intestine, but a flexible sigmoidoscopy only checks the lower third of the colon. While both tests utilize a camera-equipped tube, a colonoscopy provides a more thorough evaluation of the digestive tract.
Usual Screening Preparation Instructions
To help the provider clearly see the lining of the colon, patients follow strict preparation instructions to clear out the colon before the screening. Individuals typically begin a low-fiber diet two or three days before the appointment. This process involves eating white bread or rice, and nuts, seeds, and raw vegetables are avoided.
A bowel prep kit clears stool from the colon to allow the doctor to have a clear view of the colon tissue during the screening test. Patients consume clear liquids, such as broth, and they avoid red dyes that can be mistaken for blood during the test. Common components of preparation include:
- Laxative pills or liquids that loosen stool
- Enemas to clear the rectum
- Osmotic agents that trigger bowel contractions
- Electrolyte solutions to maintain hydration
Typical Screening Processes
Medical staff help the patient lie on their left side on an exam table. Before the doctor performs a colonoscopy, the patient typically receives sedation for comfort throughout the test. For a sigmoidoscopy, the patient may not need to be sedated. A physician inserts a thin tube called a colonoscope or sigmoidoscope into the anus, and the instrument pumps air into the colon to expand the lining; this enables the doctor to view healthy and irregular tissues as well as polyps on the monitor screen.
While a sigmoidoscopy takes about 15 minutes, a full colonoscopy often requires 30 to 45 minutes. The doctor might take small tissue samples for a biopsy. During the colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, the doctor will remove any polyps they see. This removal allows the provider to stop the removed growths from eventually causing cancer. If necessary, the doctor will recommend cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
Schedule Colon Cancer Screenings Today
Screening for this type of cancer typically begins at age 45 for individuals with an average risk level. Doctors may recommend earlier tests for high-risk patients, and these individuals should discuss their family history with a provider. To learn more about how to prepare for a colon cancer screening, consult your healthcare provider.