
Family Planning Strategies For New Parents
December 9, 2025
Innovative Approaches in Orthopedic Treatments and Sports Medicine
December 9, 2025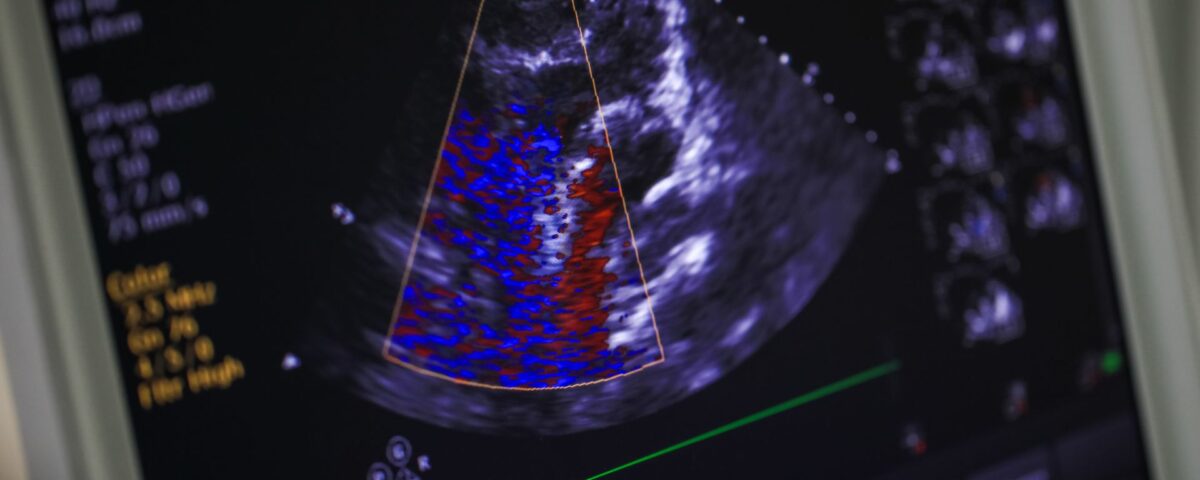
An echocardiogram is a standard diagnostic tool in cardiology used to assess the heart’s structure and function. It provides detailed images that help physicians identify various cardiac conditions. Understanding this procedure can provide clarity for patients undergoing cardiac evaluation. Here is more information on what an echocardiogram is, how it functions, and the types of problems it can detect:
What Is an Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to produce live images of your heart, so doctors can see how it is beating and pumping blood. The images show the size and shape of the heart, along with its chambers and valves. Doctors use this test to diagnose and monitor certain heart conditions by checking the heart’s chambers and valves, allowing them to evaluate the heart’s overall function. The information gathered helps in creating a personalized treatment plan.
How Does It Work?
The procedure uses ultrasound, which emits high-frequency sound waves. A device called a transducer sends sound waves through your chest toward your heart, and these waves bounce off the heart’s structures. The transducer then picks up the returning echoes, which a computer converts into images on a monitor.
What Does It Involve?
During a standard transthoracic echocardiogram, you will lie on an examination table. A technician will apply a special gel to your chest, which helps the sound waves travel more effectively. The technician then presses the transducer firmly against your skin, moving it over different areas of your chest to capture images from various angles.
The test is generally painless, though you might feel slight pressure from the transducer. It typically takes 40 to 60 minutes to complete. After the test, the gel is wiped off, and you can resume your normal activities immediately, as no recovery time is needed.
How Do They Detect Heart Problems?
Echocardiograms provide information about the heart. By examining the images, a cardiologist can assess several aspects of your heart’s health. The test shows the size and shape of your heart, and it can detect any abnormalities in the heart muscle or chambers.
A cardiologist may evaluate how well your heart is pumping blood. The test also reveals how the heart valves are functioning, identifying issues such as stenosis or regurgitation. It can detect problems with the pericardium, the outer lining of the heart, and find blood clots or tumors inside the heart.
Echocardiography is useful for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, including:
- Heart valve disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defects
- Pericardial disease
- Endocarditis
- Heart tumors
What Are the Benefits?
Echocardiograms offer several benefits as a diagnostic tool. The procedure is non-invasive, meaning it does not require any incisions or injections, which makes it a low-risk test. It does not use radiation, so it is safe for repeated use and for patients who should avoid radiation exposure, like pregnant women.
The test provides real-time images, allowing for a dynamic assessment of the heart’s function. This capability gives cardiologists immediate insight into the heart’s mechanical operations. The detailed information obtained from an echocardiogram helps formulate an accurate diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.
Visit a Cardiologist Today
An echocardiogram is a standard and effective procedure for evaluating heart health and detecting various cardiac problems. It uses sound waves to create images of the heart, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of its structure and function. If you are experiencing symptoms or have risk factors for heart disease, consult a specialist. A cardiologist can determine if an echocardiogram is appropriate for your situation.
