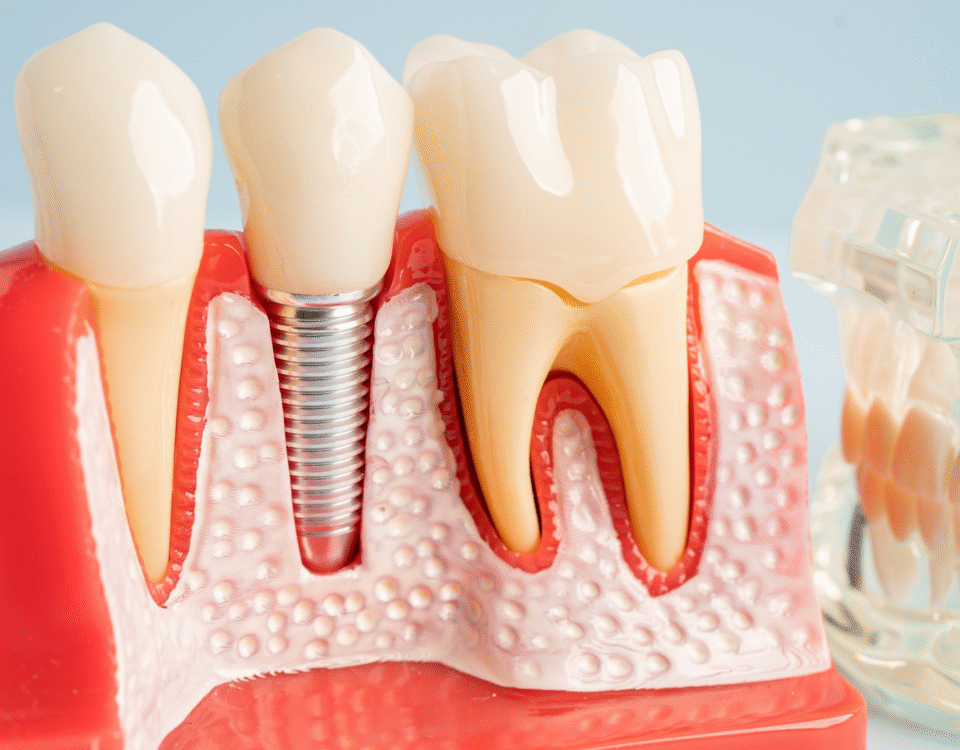
Cosmetic Dentistry Solutions for Smile Improvement
September 26, 2025
When to Visit a Dermatologist for Skin Rashes
September 26, 2025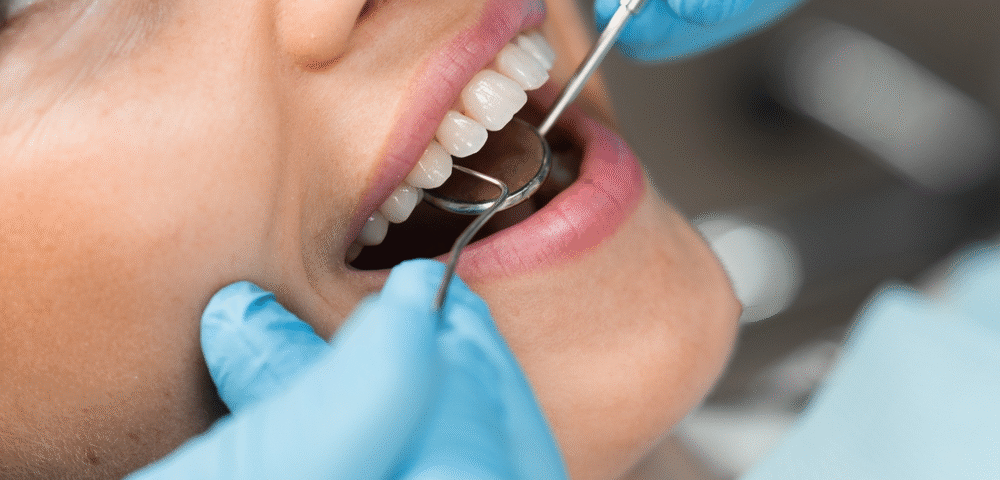
Oral health is one of the most important parts of your overall well-being, but it is often ignored until problems become painful. Among the most common dental issues worldwide are cavities and gum disease. These problems may start small, but if left untreated, they can lead to serious discomfort, tooth loss, and even affect your general health. The good news is that modern dentistry offers a variety of treatments to manage and prevent these issues.
In this article, we’ll explore dentistry treatments for cavities and gum disease in detail, how they work, and why timely dental care matters.
Understanding Cavities and Gum Disease
Before diving into treatments, it’s important to understand what these dental issues actually are.
What Are Cavities?
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are small holes or areas of decay in the teeth. They develop when plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—builds up on teeth and breaks down enamel with acids. Eating sugary or starchy foods increases this risk. If untreated, cavities can progress deeper, damaging the tooth structure and nerves.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, affects the gums and bone that support your teeth. It starts with gingivitis, which is the inflammation of the gums. If not managed early, it can progress to periodontitis, a more serious condition where the gums pull away from the teeth, bone is lost, and teeth may loosen or fall out.
Dentistry Treatments for Cavities
Dentists use different treatments depending on how advanced the cavity is.
1. Fluoride Treatments
For very early-stage cavities, fluoride treatments can sometimes reverse damage. Dentists may apply fluoride varnish, gel, or foam to strengthen enamel and stop the cavity from progressing. This treatment is especially common for children but can help adults as well.
2. Dental Fillings
When cavities become too large for fluoride alone, dentists clean out the decayed area and fill it with a material like composite resin, amalgam, or ceramic. Fillings restore tooth function and prevent further decay. Composite (tooth-colored) fillings are popular because they blend naturally with teeth.
3. Dental Crowns
If a cavity has severely weakened a tooth, a crown may be necessary. A crown is a cap that covers the entire tooth to restore strength, shape, and appearance. Crowns can be made of porcelain, ceramic, or metal.
4. Root Canal Treatment
If decay reaches the inner pulp of the tooth, it can cause extreme pain and infection. In this case, a dentist or endodontist may perform a root canal, where the infected pulp is removed, the inside is cleaned, and the tooth is sealed. A crown is usually placed afterward for protection.
5. Tooth Extraction
When a cavity destroys a tooth beyond repair, extraction is the last option. The missing tooth can then be replaced with a dental implant, bridge, or denture.
Dentistry Treatments for Gum Disease
Treatments for gum disease vary depending on whether it is gingivitis or more advanced periodontitis.
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
During early stages, a regular professional cleaning by a dentist or hygienist can remove plaque and tartar buildup. Along with improved brushing and flossing at home, this can reverse gingivitis.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
For more advanced gum disease, dentists perform scaling and root planing (deep cleaning). Scaling removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line, while root planing smooths tooth roots so gums can reattach more easily.
3. Medications
Dentists may prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobial mouth rinses to reduce infection and inflammation. Sometimes, small antibiotic gels or chips are placed directly into gum pockets.
4. Gum Surgery
When gum disease becomes severe, surgery may be needed. Common surgical treatments include:
- Flap surgery: Lifting gums to remove tartar and bacteria, then stitching them back in place.
- Gum grafts: Transplanting gum tissue to cover exposed roots and reduce sensitivity.
- Bone grafts: Adding bone material to areas where gum disease has caused bone loss.
5. Laser Therapy
Some dentists now use laser technology to remove diseased gum tissue and promote healing. Laser therapy is less invasive and can reduce discomfort compared to traditional surgery.
Preventive Care: The Best Treatment
Although dentistry has many effective treatments, prevention is always better. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits can greatly reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
- Visit the dentist every six months for checkups and cleanings.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks that feed cavity-causing bacteria.
- Avoid smoking, as it increases the risk of gum disease.
Table: Comparing Treatments for Cavities and Gum Disease
| Condition | Early Treatment | Advanced Treatment | Severe Stage Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cavities | Fluoride treatment | Fillings / Crowns | Root canal / Tooth extraction |
| Gum Disease | Professional cleaning (gingivitis) | Scaling & root planing, medications | Surgery / Laser therapy |
Why Timely Treatment Matters
Delaying dental care for cavities or gum disease can lead to bigger problems. For cavities, untreated decay can spread to other teeth or even cause infections in the jaw and bloodstream. For gum disease, untreated periodontitis can result in tooth loss and has been linked to heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems.
Taking action early not only saves your teeth but also protects your overall health and reduces the need for expensive procedures later.
FAQs About Dentistry Treatments for Cavities and Gum Disease
1. Can cavities heal on their own without treatment?
No, once a cavity forms beyond the very early stage, it cannot heal naturally. Professional dental treatment is needed to stop the decay.
2. How painful are gum disease treatments like scaling and root planing?
Most patients experience little to mild discomfort, especially with local anesthesia. Discomfort usually fades after a few days.
3. How long does a dental filling last?
It depends on the material and care. Composite fillings last about 5–10 years, while amalgam or ceramic can last longer with proper oral hygiene.
4. Can gum disease be completely cured?
Gingivitis can be reversed with proper care, but advanced periodontitis cannot be fully cured. However, it can be managed to prevent further damage.
5. Is laser treatment better than traditional gum surgery?
Laser therapy is less invasive and may cause less discomfort, but it is not suitable for all cases. A dentist will recommend the best option based on severity.
Conclusion
Cavities and gum disease are two of the most common dental problems, but they don’t have to control your life. Thanks to modern dentistry, there are effective treatments at every stage—from simple fluoride applications to advanced gum surgery. The key is catching problems early, maintaining regular dental visits, and practicing good oral hygiene every day.
By taking care of your teeth and gums, you’re not only protecting your smile but also supporting your overall health for years to come.